File:Dissociative identity disorder neuroscience brain imaging.png
Dissociative_identity_disorder_neuroscience_brain_imaging.png (696 × 466 pixels, file size: 361 KB, MIME type: image/png)
This file is from Wikimedia Commons and may be used by other projects. The description on its file description page there is shown below.
Summary
| DescriptionDissociative identity disorder neuroscience brain imaging.png |
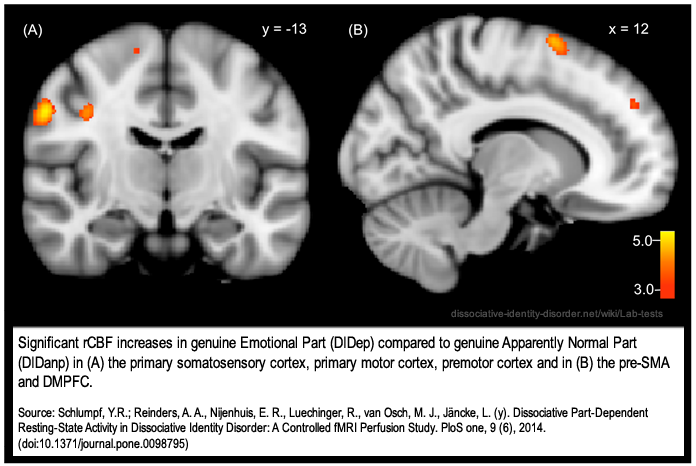
English: In accordance with the Theory of Structural Dissociation of the Personality (TSDP), studies of dissociative identity disorder (DID) have documented that two prototypical dissociative subsystems of the personality, the “Emotional Part” (EP) and the “Apparently Normal Part” (ANP), have different biopsychosocial reactions to supraliminal and subliminal trauma-related cues and that these reactions cannot be mimicked by fantasy prone healthy controls nor by actors.
Conclusion: DID involves dissociative part-dependent resting-state differences. Compared to ANP, EP activated brain structures involved in self-referencing and sensorimotor actions more. Actors had different perfusion patterns compared to genuine ANP and EP. Comparisons of neural activity for individuals with DID and non-DID simulating controls suggest that the resting-state features of ANP and EP in DID are not due to imagination. The findings are consistent with TSDP and inconsistent with the idea that DID is caused by suggestion, fantasy proneness, and role-playing Results from Schlumpf, Y.R.; Reinders, A. A., Nijenhuis, E. R., Luechinger, R., van Osch, M. J., Jäncke, L. (y). Dissociative Part-Dependent Resting-State Activity in Dissociative Identity Disorder: A Controlled fMRI Perfusion Study. PloS one, 9 (6), 2014. (doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0098795) Journal source http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0098795 Figure 1: Significant rCBF increases in genuine EP (DIDep) compared to genuine ANP (DIDanp) in (A) the primary somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex, premotor cortex and in (B) the pre-SMA and DMPFC. rCBF = regional cerebral blood flow. |
| Date | |
| Source | https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0098795 |
| Author |
Significant rCBF increases in genuine EP (DIDep) compared to genuine ANP (DIDanp) in (A) the primary somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex, premotor cortex and in (B) the pre-SMA and DMPFC. Source: Schlumpf, Y.R.; Reinders, A. A., Nijenhuis, E. R., Luechinger, R., van Osch, M. J., Jäncke, L. (y). Dissociative Part-Dependent Resting-State Activity in Dissociative Identity Disorder: A Controlled fMRI Perfusion Study. PloS one, 9 (6), 2014. (doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0098795) Modification by "DID is real": caption with border. |
| Permission (Reusing this file) |
See Figures section |
Licensing
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- share alike – If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same or compatible license as the original.
Captions
Items portrayed in this file
depicts
3 August 2014
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 15:05, 7 October 2014 |  | 696 × 466 (361 KB) | Phil2007 | User created page with UploadWizard |
Pages using this file
The following page uses this file:
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it.
If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Author | Trauma and Dissociation Project, Trauma and Dissociation wiki http://dissociative-identity-disorder.net |
|---|---|
| Copyright holder |
|
| Image title |
|
| Software used |
|
| File change date and time | 22:39, 3 August 2014 |
| Date and time of digitizing | 11:58, 31 August 2013 |
| Short title |
|
| Keywords |
|
| Writer | Trauma and Dissociation Project |
| Copyright status | Copyrighted |
| Online copyright statement | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/ |
| Horizontal resolution | 121.65 dpc |
| Vertical resolution | 121.65 dpc |