Vertically Transmitted Infection
| Live, reproduce, die Biology |
| Life as we know it |
| Divide and multiply |
| Great Apes |
A vertically transmitted infection is a type of infection which goes through the process of vertical transmission (also called transplacental transmission and perinatal transmission) whereby a pathogen is spread from a parent to its baby, embryo or fetus before or after birth.[1] It can occur when the parent in question became infected by a pathogen or suffers from a pre-existing condition. This means that vertical transmission can occur in utero, peripartum, and postnatal. Viruses, bacteria, and other organisms are all able to spread through vertical transmission.
Routes[edit]
As stated previously, the main routes of vertical transmission may be across the placenta (hence why vertical transmission may also occasionally be called transplacental transmission) or in the birth canal (the cervix, vagina, and vulva), but it can also occur due to amniocentesis, chestfeeding (since a pathogen, such as HIV, can spread through chest milk)[2] or major trauma.[3]
Vertically transmitted infections[edit]
There is a wide range of vertically transmitted infections in existence, which include but are not limited to:
- Enteroviruses[4]
- Chlamydia (albeit seldom)[5]
- Cytomegalovirus[6]
- HBV (Hepatitis B)[7][8]
- HCV (Hepatitis C)[9][10] (To the point where there's a need for babies to be tested for HCV infection if the parent has HCV antibodies!)[11]
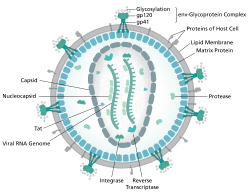
- HIV (both HIV-1 and HIV-2)[12][13][14][15][16]
- Rubella[17]
- Syphilis[18]
- HPV[19]
- HSV (Herpes Simplex Viruses; known colloquially as Herpes)[20][21]
- Parvovirus B19[22]
- Zikavirus[23]
The acronym ‘TORCH’ refers to Toxoplasma gondii, other (any unmentioned pathogen capable of being vertically transmitted), rubella virus, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex virus. It includes bacteria, viruses and parasites — however it isn't perfect, as a wide variety of pathogens would be listed as "other."[24]
Ways to allay the chance of vertical transmission[edit]
It goes without saying that pregnant people ought to be vaccinated against hepatitis A, hepatitis B, rubella, varicella[note 1] and HPV prior to getting pregnant. In earnest, if you have the privilege to easily access vaccines, yet you assiduously refuse to be inoculated, you shouldn't be a parent. Prenatal care is also paramount in order to protect the pregnancy; you are able to start receiving it as soon as you know you're pregnant.[25] Make sure you're tested for various antibodies against vertically transmitted infections; they can indicate that you've come into contact with a vertically transmitted infection during gestation.
For example, to prevent vertical transmission of HIV (the virus that causes AIDS), prenatal testing, prenatal antiretroviral therapy/antiretroviral (ARV) drugs, cesarean delivery (also known as a C-section), avoidance of chestfeeding, and other preventative measures are all advised.[26]
Notes[edit]
- ↑ Note that varicella causes both chickenpox and shingles/herpes zoster, therefore, you need to get both the chickenpox and shingles vaccines.
References[edit]
- ↑ "Medical Definition of Vertical transmission." MedicineNet, 3 Dec. 2021, https://www.medicinenet.com/vertical_transmission/definition.htm.
- ↑ "Perinatal Transmission." HIV.gov, 4 Dec. 2021, https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/en/glossary/perinatal-transmission
- ↑ Fermin, Gustavo. "Chapter 5 - Host Range, Host–Virus Interactions, and Virus Transmission." ScienceDirect, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978012811257100005X. Accessed 3 December 2021.
- ↑ Lozovskaia, L S et al. “Znachenie vertikal'noĭ peredachi énterovirusov v épidemiologii vrozhdennykh virusnykh infektsiĭ” [The importance of the vertical transmission of enteroviruses in the epidemiology of congenital viral infections]. Akusherstvo i ginekologiia ,2 (1995): 26-30.
- ↑ Honkila, Minna et al. “Probability of vertical transmission of Chlamydia trachomatis estimated from national registry data.” Sexually transmitted infections vol. 93,6 (2017): 416-420. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2016-052884 (Link: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28228485/)
- ↑ Pass, Robert F, and Brenna Anderson. “Mother-to-Child Transmission of Cytomegalovirus and Prevention of Congenital Infection.” Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society vol. 3 Suppl 1,Suppl 1 (2014): S2-6. doi:10.1093/jpids/piu069
- ↑ Gentile, Ivan, and Guglielmo Borgia. “Vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus: challenges and solutions.” International journal of women's health vol. 6 605-11. 10 Jun. 2014, doi:10.2147/IJWH.S51138
- ↑ Mavilia, Marianna G, and George Y Wu. “Mechanisms and Prevention of Vertical Transmission in Chronic Viral Hepatitis.” Journal of clinical and translational hepatology vol. 5,2 (2017): 119-129. doi:10.14218/JCTH.2016.00067
- ↑ "Increased Risk for Mother-to-Infant Transmission of Hepatitis C Virus Among Medicaid Recipients ― Wisconsin, 2011–2015.", Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 3 Dec. 2021, https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/66/wr/mm6642a3.htm.
- ↑ “Vertical transmission of the hepatitis C virus: Current knowledge and issues.” Paediatrics & child health vol. 13,6 (2008): 529-41.
- ↑ Yeung, Chun-Yan et al. “Vertical transmission of hepatitis C virus: Current knowledge and perspectives.” World journal of hepatology vol. 6,9 (2014): 643-51. doi:10.4254/wjh.v6.i9.643
- ↑ Newell, M L. “Vertical transmission of HIV-1 infection.” Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene vol. 94,1 (2000): 1-2. doi:10.1016/s0035-9203(00)90413-9
- ↑ "Perinatal (Mother-to-Child) HIV Transmission." Minnesota Department of Health, 3 Dec. 2021, https://www.health.state.mn.us/diseases/hiv/prevention/perinatal.html
- ↑ Gilroy, Shelley. "How is vertical transmission of HIV-2 prevented?" Medscape, https://www.medscape.com/answers/211316-6167/how-is-vertical-transmission-of-hiv-2-prevented. Accessed 4 December 2021.
- ↑ Gilroy, Shelley. "What is the mother-to-child transmission rate of HIV-2 in France?" Medscape, https://www.medscape.com/answers/211316-6168/what-is-the-mother-to-child-transmission-rate-of-hiv-2-in-france. Accessed 4 December 2021.
- ↑ M. Burgard, C. Jasseron, S. Matheron, F. Damond, K. Hamrene, S. Blanche, A. Faye, C. Rouzioux, J. Warszawski, L. Mandelbrot, the ANRS French Perinatal Cohort EPF-CO1, Mother-to-Child Transmission of HIV-2 Infection from 1986 to 2007 in the ANRS French Perinatal Cohort EPF-CO1, Clinical Infectious Diseases, Volume 51, Issue 7, 1 October 2010, Pages 833–843, https://doi.org/10.1086/656284
- ↑ "Transmission." Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 3 Dec. 2021, https://www.cdc.gov/rubella/about/transmission.html.
- ↑ Cerqueira, Luciane Rodrigues Pedreira de et al. “The magnitude of syphilis: from prevalence to vertical transmission.” Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de Sao Paulo vol. 59 e78. 21 Dec. 2017, doi:10.1590/S1678-9946201759078
- ↑ Lee, Seung Mi et al. “Risk of vertical transmission of human papillomavirus throughout pregnancy: a prospective study.” PloS one vol. 8,6 e66368. 13 Jun. 2013, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066368
- ↑ Bhatta, Anil Kumar et al. “Vertical transmission of herpes simplex virus: an update.” Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft = Journal of the German Society of Dermatology : JDDG vol. 16,6 (2018): 685-692. doi:10.1111/ddg.13529
- ↑ Jones, Cheryl A. “Vertical transmission of genital herpes: prevention and treatment options.” Drugs vol. 69,4 (2009): 421-34. doi:10.2165/00003495-200969040-00003
- ↑ Puccetti, C et al. “Parvovirus B19 in pregnancy: possible consequences of vertical transmission.” Prenatal diagnosis vol. 32,9 (2012): 897-902. doi:10.1002/pd.3930
- ↑ "Zika in Infants & Children." Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 5 Dec. 2021, https://www.cdc.gov/pregnancy/zika/testing-follow-up/zika-in-infants-children.html
- ↑ Megli, C.J., Coyne, C.B. Infections at the maternal–fetal interface: an overview of pathogenesis and defence. Nat Rev Microbiol (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-021-00610-y
- ↑ "Prenatal Care." Planned Parenthood, 5 Dec. 2021, https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/pregnancy/prenatal-care
- ↑ Gilroy, Shelley. "What are vertical transmission prevention measures for HIV infection?" Medscape, https://www.medscape.com/answers/211316-6165/what-are-vertical-transmission-prevention-measures-for-hiv-infection. Accessed 4 December 2021.