There is no RationalWiki without you. We are a small non-profit with no staff—we are hundreds of volunteers who document pseudoscience and crankery around the world every day. We will never allow ads because we must remain independent. We cannot rely on big donors with corresponding big agendas. We are not the largest website around, but we believe we play an important role in defending truth and objectivity. |
Fighting pseudoscience isn't free. We are 100% user-supported! Help and donate $5, $10, $20 or whatever you can today with |
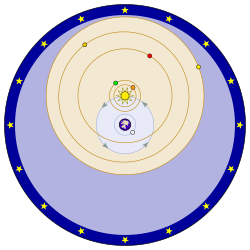
Geocentrism
| The fault in our stars Pseudoastronomy |
| Adding epicycles |
| Epicyclists |
“”For most of our history we had grave misconceptions about exactly where Earth stood within the cosmos. Due to scientific limitations and more than a touch of narcissism, we believed everything in the universe literally revolved around us. It was a theory called geocentrism, which was originally egocentrism, but they spelled it wrong.
|
| —The Daily Show with Jon Stewart |
Geocentrism is the belief that the Sun, the planets and all the stars revolve around the Earth. It used to be the standard model of the Universe from ancient times until the 17th-18th centuries, when new evidence (especially after the invention of the telescope) convinced most "natural philosophers" (i.e., early scientists) that the Earth revolved around the Sun instead.
Religious institutions took longer to be convinced, with some of them still endorsing geocentrism centuries after it became laughably discredited. And, believe it or not, a few cranks still hold on to it today. You can thank the Old Testament for the lingering belief in this one. It has at least four verses claiming that the Earth "cannot be moved," and one stating that the Sun goes around the earth. Modern Geocentrism is often, but not always, coupled with the belief that the Earth is flat. Geocentrism should not be confused with egocentrism, which is the belief that the Sun, the stars, the other planets and the Earth all revolve around oneself (metaphorically, of course).
History
Geocentrism was the standard model throughout the Western world during antiquity, the Middle Ages and the Renaissance. The earliest known attempt at a mathematical model came from Eudoxus of Cnidus![]() in the 4th century BCE (his works are lost, but his solar system is described by Aristotle)[1].
in the 4th century BCE (his works are lost, but his solar system is described by Aristotle)[1].
Aristarchus of Samos was the first person to challenge the geocentric model, suggesting a heliocentric Universe in the 3rd century BCE but he had little following, and it is unknown whether he proposed a mathematical model in line with Eudoxus or a philosophical model, more in line with Pythagorean speculations which put the "central fire" at the center of the Universe. Aristarchus' original work is lost,[2] and its existence is known only because Archimedes makes a fairly nondescript reference to it (Aristarchus of Samos brought out a book consisting of some hypotheses, in which the premises lead to the result…[3]). Ptolemy's mathematical theory of the Solar System placed all celestial bodies orbiting in a circle called a deferent, the circle centered on a halfway point between the Earth and another empty point called an equant. While this system may not sound strictly Geocentric, this strange positioning was used to explain the changes in motion across the sky that result from the fact that orbits are not, in fact, perfectly circular. In addition, some planets appear to reverse direction at certain points in their orbit; Ptolemy accounted for this "retrograde motion" by adding that the planets orbit around a sub-circle that travels along the deferent, called an "epicycle". Ptolemy was unknowingly doing a very primitive version of a modern technique called Fourier Analysis, where it turns out that just about any shape can be created by large numbers of circles within circles.[4][5]
In the interim between Ptolemy and Copernicus, Martianus Capella noted in the 4th century CE that Mercury and Venus do not appear to move far from the Sun, and suggested a third sort of model called Geoheliocentrism![]() , which failed to achieve notoriety (though it was known to Medieval and early modern astronomers, with both Copernicus and Kepler referring to Capella; this system is often erroneously attributed to Heraclides of Pontus, a contemporary of Eudoxus[6]).
, which failed to achieve notoriety (though it was known to Medieval and early modern astronomers, with both Copernicus and Kepler referring to Capella; this system is often erroneously attributed to Heraclides of Pontus, a contemporary of Eudoxus[6]).
The ancient Greeks noted that if the Earth did move around the Sun, the stars should appear to shift their positions from one part of the year to the next (parallax), a phenomenon they failed to observe. Alternatively the stars would have to be so ridiculously far away that the shift in position was too small to be seen by the naked eye, which would make for a ludicrously large empty space between the most distant known planet, Saturn, and the "fixed stars". Measurements dependent on naked-eye instruments could detect a parallax of something like one arc-minute, which meant that the distance to the "fixed stars" had to be at least 700 times larger than the distance to Saturn if the Earth moved around the Sun.[7]:201 The ancient Greeks dismissed this possibility as absurd, but of course, today we know that the stars are in fact much farther away than that. The early modern astronomer Tycho Brahe also dismissed this possibility, citing that in a heliocentric system, the disk sizes and brightness of stars (Procyon was used as a particular example) would require them to be either close enough to measure parallax (which had still not been discovered; Procyon, for instance, has a parallax of 0.286 arcseconds, or about 0.5% of the maximum parallax that the Greeks could detect; such accuracy was beyond even Tycho, with his much better measuring capacity), or to be substantially larger than the Sun, making most or all of the stars enormously larger than the Sun, which he dismissed as absurd.[8] This objection is solved not only by the enormous distance between stars, but by the fact that the "disk" of a star (other than the Sun) is an optical illusion caused by diffraction of light, called an Airy Disk;![]() the idea that they were illusory was suggested by Galileo Galilei, but the hypothesis lacked evidence or a physical mechanism until Airy's work, 200 years after Tycho and Galileo.
the idea that they were illusory was suggested by Galileo Galilei, but the hypothesis lacked evidence or a physical mechanism until Airy's work, 200 years after Tycho and Galileo.
Some late Medieval scholars, notably Nicholas of Cusa and Nicolas Oresme,[9] brought up the possibility that the Earth might move, but Copernicus was the one who really revived heliocentrism in 1514 in his Commentariolus, drawing on Aristarchus.[10] Copernicus' Heliocentric system removed the Equant of the Ptolemaic system, but was still reliant on epicycles (even adding an epicycle to an epicycle, in the case of the Moon[11]). Galileo promoted a physical interpretation of the Copernican theory in the following century, provoking hostility from the Church who denounced it as heresy. Due to this controversy, Copernicus's book was still listed on the Index (the list of books banned by the Catholic Church, though at this point in time, a book on the Index could still be read if it were "corrected", according to the desires of the Congregation of the Index[12]) between 1616 and 1758.
Victory of heliocentrism
It was a mixture of different reasons that led to the final victory of Heliocentrism (symbolized by the Catholic Church's capitulation in 1758, though most working astronomers made the switch a century earlier). In 1551, the astronomer Erasmus Reinhold published the Prutenic Tables,![]() computed by the Copernican model, which failed to improve on the Alphonsine Tables based on Ptolemaic astronomy (which one could expect, as the Prutenic Tables were based on the same underlying data as the Alphonsine Tables, and that data had been corrupted by the accumulation of pre-printing press copyist errors over the centuries).[13][14] In 1588, Tycho Brahe and Ursus
computed by the Copernican model, which failed to improve on the Alphonsine Tables based on Ptolemaic astronomy (which one could expect, as the Prutenic Tables were based on the same underlying data as the Alphonsine Tables, and that data had been corrupted by the accumulation of pre-printing press copyist errors over the centuries).[13][14] In 1588, Tycho Brahe and Ursus![]() both published new models which revived Capella's geoheliocentric idea, and extended it to encompass all heavenly bodies except the Moon, Sun, and fixed stars (the only true difference between Ursus' and Tycho's models were that the former also claimed the Earth rotated on its axis, and the latter had a completely stationary Earth; there was a bitter dispute in which Tycho accused Ursus of plagiarism). In 1595, Johannes Kepler published his Mysterium Cosmographicum, defending the Copernican model and positing a heliocentric Universe in which the planetary orbits are bounded within the six platonic solids, as a geometric basis for the Universe. Five years later in 1600, William Gilbert proposed a new geocentric model in his De Magnete, which was Ptolemaic but gave the Earth a daily rotational motion.[15] This, too, was considered and rejected by other scholars; if Earth rotates, then one expects a Coriolis deflection in objects dropped from heights (this does in fact happen, but would not be directly observed until the end of the 18th century). Kepler, who had a mystical belief in the Sun as the primary source of motive force in the Universe,[16] appealed to De Magnete, which hypothesized that magnetism from the Earth (which Gilbert referred to as its "magnetic virtue") induced the orbits of the heavenly bodies around it.[15] In the process, he finally took the necessary step that would ultimately vindicate heliocentrism; Kepler removed the epicycles and circular orbits, and proposed that planetary orbits are elliptical. His Astronomia Nova (containing his first two Laws of Planetary Motion) was completed around 1606 and published in 1609, to a lukewarm reception. Along the way, Kepler published a verbose volume called Ad vitellionem paralipomena quibus astronomiae pars optica traditor, in which the first proposal of the inverse square law for the propagation of light is made,[17] later to be repurposed by Ismael Boulliau[18] and Isaac Newton for gravity (the former speculated and rejected the hypothesis; the latter incorporated it into a larger system of physics).
both published new models which revived Capella's geoheliocentric idea, and extended it to encompass all heavenly bodies except the Moon, Sun, and fixed stars (the only true difference between Ursus' and Tycho's models were that the former also claimed the Earth rotated on its axis, and the latter had a completely stationary Earth; there was a bitter dispute in which Tycho accused Ursus of plagiarism). In 1595, Johannes Kepler published his Mysterium Cosmographicum, defending the Copernican model and positing a heliocentric Universe in which the planetary orbits are bounded within the six platonic solids, as a geometric basis for the Universe. Five years later in 1600, William Gilbert proposed a new geocentric model in his De Magnete, which was Ptolemaic but gave the Earth a daily rotational motion.[15] This, too, was considered and rejected by other scholars; if Earth rotates, then one expects a Coriolis deflection in objects dropped from heights (this does in fact happen, but would not be directly observed until the end of the 18th century). Kepler, who had a mystical belief in the Sun as the primary source of motive force in the Universe,[16] appealed to De Magnete, which hypothesized that magnetism from the Earth (which Gilbert referred to as its "magnetic virtue") induced the orbits of the heavenly bodies around it.[15] In the process, he finally took the necessary step that would ultimately vindicate heliocentrism; Kepler removed the epicycles and circular orbits, and proposed that planetary orbits are elliptical. His Astronomia Nova (containing his first two Laws of Planetary Motion) was completed around 1606 and published in 1609, to a lukewarm reception. Along the way, Kepler published a verbose volume called Ad vitellionem paralipomena quibus astronomiae pars optica traditor, in which the first proposal of the inverse square law for the propagation of light is made,[17] later to be repurposed by Ismael Boulliau[18] and Isaac Newton for gravity (the former speculated and rejected the hypothesis; the latter incorporated it into a larger system of physics).
Galileo's telescopic observations (announced beginning in his 1610 Starry Messenger![]() ) revealed the heavens to be different from the traditional conceptions: the phases of Venus, mountains on the Moon, satellites of Jupiter and spots on the Sun. The heavens could never again be regarded as totally different from Earth. The phases of Venus in particular definitively knocked out the ancient Ptolemaic system and the much more recent Gilbertian system, which had no way of explaining the observed phases of Venus based on its position near the Sun in those systems. Some interpreted this as evidence for Heliocentrism, but the phases could be accounted for in the geoheliocentric systems of Cappela, Tycho, and Ursus. Lacking a solution to the parallax/apparent size problem, most astronomers switched to the Geoheliocentric systems (primarily the Tychonic System). The Tychonic System became the default model for most Astronomers, but this state of affairs slowly began to change after Kepler's publication of the Rudolphine Tables in 1627, calculated using Kepler's Heliocentric model, based on Tycho's data from his Uraniborg Observatory on Hven. Not being based on the corrupted data used in the Alphonsine and Prutenic tables, the Rudolphine tables, and therefore Kepler's Heliocentric model, were more accurate and (by virtue of being mathematically much simpler) substantially easier to use. Though the 1616 prohibition prevented Astronomers in Catholic countries from claiming that Heliocentrism is physical reality, they were not prevented from using the Keplerian system instrumentally and by around the 1660s, the Keplerian system had overthrown the geoheliocentric systems. Newton's 1687 Principia
) revealed the heavens to be different from the traditional conceptions: the phases of Venus, mountains on the Moon, satellites of Jupiter and spots on the Sun. The heavens could never again be regarded as totally different from Earth. The phases of Venus in particular definitively knocked out the ancient Ptolemaic system and the much more recent Gilbertian system, which had no way of explaining the observed phases of Venus based on its position near the Sun in those systems. Some interpreted this as evidence for Heliocentrism, but the phases could be accounted for in the geoheliocentric systems of Cappela, Tycho, and Ursus. Lacking a solution to the parallax/apparent size problem, most astronomers switched to the Geoheliocentric systems (primarily the Tychonic System). The Tychonic System became the default model for most Astronomers, but this state of affairs slowly began to change after Kepler's publication of the Rudolphine Tables in 1627, calculated using Kepler's Heliocentric model, based on Tycho's data from his Uraniborg Observatory on Hven. Not being based on the corrupted data used in the Alphonsine and Prutenic tables, the Rudolphine tables, and therefore Kepler's Heliocentric model, were more accurate and (by virtue of being mathematically much simpler) substantially easier to use. Though the 1616 prohibition prevented Astronomers in Catholic countries from claiming that Heliocentrism is physical reality, they were not prevented from using the Keplerian system instrumentally and by around the 1660s, the Keplerian system had overthrown the geoheliocentric systems. Newton's 1687 Principia![]() then puts the mechanics of the Solar System on a secure mathematical and physical basis: Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion, upon which his model is based, can be derived from Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation (including the 2nd Law, which posits that planets sweep out equal areas in equal times, the only one of Kepler's Laws still in dispute). With this, the Aristotelian claim of a demarcation between the sublunar and superlunar spheres is finally struck down: physics is the same everywhere in the Universe.
then puts the mechanics of the Solar System on a secure mathematical and physical basis: Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion, upon which his model is based, can be derived from Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation (including the 2nd Law, which posits that planets sweep out equal areas in equal times, the only one of Kepler's Laws still in dispute). With this, the Aristotelian claim of a demarcation between the sublunar and superlunar spheres is finally struck down: physics is the same everywhere in the Universe.
At this point, Heliocentrism has been accepted, initially instrumentally due to ease of use and simplicity, and post-Principia, with good reason to suggest that Heliocentrism is not merely instrumentally useful, but a true physical representation of the Solar System. The only thing missing was a direct demonstration of the Earth's motion; the predicted parallax, the oldest and most substantial objection to Heliocentrism, has yet to be observed. In 1729, the lack of empirical evidence is solved in a completely unanticipated way: James Bradley discovers stellar aberration![]() in γ-Draconis, providing direct physical evidence of the Earth's motion, and measuring its orbital velocity.[19][7] Bradley's paper was translated several years later into Italian, but despite the direct evidence, Catholic astronomers were still barred by the 1616 prohibition on Copernicanism from acknowledging it as physically correct. In 1758, 30 years after Bradley's publication, the Church capitulates, and removes Copernicanism from the Index (This was done with no apology to Galileo; the apology wouldn't occur for another 234 years, in 1992). The long awaited parallax was finally discovered by Friedrich Bessel in 1838, reporting a parallax of 0.3136±0.0136 arcseconds in 61 Cygni. It should be noted that before the discoveries of physical evidence to justify heliocentrism as fact, geocentric astronomy was more of a protoscience than pseudoscience. But with the discoveries of stellar aberration, Coriolis deflection, and stellar parallax, geocentrism (as well as an irrotational Earth), geocentrism was completely relegated to the backwaters of physics crankery and pseudoastronomy, where it remains today.
in γ-Draconis, providing direct physical evidence of the Earth's motion, and measuring its orbital velocity.[19][7] Bradley's paper was translated several years later into Italian, but despite the direct evidence, Catholic astronomers were still barred by the 1616 prohibition on Copernicanism from acknowledging it as physically correct. In 1758, 30 years after Bradley's publication, the Church capitulates, and removes Copernicanism from the Index (This was done with no apology to Galileo; the apology wouldn't occur for another 234 years, in 1992). The long awaited parallax was finally discovered by Friedrich Bessel in 1838, reporting a parallax of 0.3136±0.0136 arcseconds in 61 Cygni. It should be noted that before the discoveries of physical evidence to justify heliocentrism as fact, geocentric astronomy was more of a protoscience than pseudoscience. But with the discoveries of stellar aberration, Coriolis deflection, and stellar parallax, geocentrism (as well as an irrotational Earth), geocentrism was completely relegated to the backwaters of physics crankery and pseudoastronomy, where it remains today.
For the Bible tells us so
Biblical assumptions
Several Biblical passages imply geocentricity, depending on how one interprets these passages. In order of their appearances in the traditional canonical order, we find:
- Joshua 10:12-13: On the day the LORD gave the Amorites over to Israel, Joshua said to the LORD in the presence of Israel: "O sun, stand still over Gibeon, O moon, over the Valley of Aijalon." So the sun stood still, and the moon stopped, till the nation avenged itself on its enemies, as it is written in the Book of Jashar. The sun stopped in the middle of the sky and delayed going down about a full day.
- 1 Chronicles 16:30: Fear before him, all the earth: the world also shall be stable, that it be not moved.
- Psalm 19:6: It [the sun] rises at one end of the heavens and makes its circuit to the other; nothing is hidden from its heat.
- Psalm 93:1: The LORD reigneth, he is clothed with majesty; the LORD is clothed with strength, wherewith he hath girded himself: the world also is established, that it cannot be moved.
- Psalm 96:10: Say among the heathen that the LORD reigneth: the world also shall be established that it shall not be moved: he shall judge the people righteously.
- Psalm 104:5: (Bless the LORD…) Who laid the foundations of the earth, that it should not be removed for ever.
- Ecclesiastes 1:5: The sun also ariseth, and the sun goeth down, and hasteth to his place where he arose.
It is difficult to explain these as obvious metaphors, when for a couple of thousand years, up until the beginnings of modern science, no one commented on their being metaphors. Everyone believed that the Sun went around a stationary Earth, and thought that that was what the Bible was saying.
What the Bible does not tell us
The Bible has little interest in the planets (nasty, messy things, far too closely associated with divination and similarly frowned-upon astrological pursuits). And no one suggests that the Bible supports the Tychonian model of the Solar System. However, it is also not true that the Bible supports any model of the movements of the planets; not, in particular, the Ptolemaic system. In fact, as Galileo pointed out, if one carefully examines the story of Joshua, it is inconsistent with the motion of the Sun in that model.[20] One must go beyond the Bible for any model of the movements of the heavens.
Modern geocentrism
In the modern world, small subsets of Biblical literalists and other scientifically illiterate cranks promote some form of geocentric worldview, although the details of their explanations vary.
Geocentric models claim the Earth does not move at all, which means that the entire Universe revolves around the earth daily. (This would mean that the stars and galaxies revolve around the Earth once every 24 hours, despite modern astronomy demonstrating that they are many light-years away and would therefore have to race round faster than light.[notes 1]) A person can take a relativistic view, that "all motion is relative", and claim one cannot tell the difference between the Earth being in motion and it being fixed. This has the drawback that it rescues the Bible's statements from being false by saying that they are meaningless. This is generally felt not any better.
The previous paragraph assumes that the universe in the geocentric model is as big as the heliocentric model demands it to be.
Twenty-first century believers in a fixed earth distance themselves from the Ptolemaic system. Some call their model "geocentricity" in an attempt to make that clear. They almost always adopt the Tychonic System: the Sun revolves around the Earth, but the planets revolve around the Sun. The Bible says nothing about the motions of the planets (and the stars), so any description of the movements of the heavenly bodies can fit the Bible, as long as the Earth is fixed and the Sun is in a closed path around the Earth. Robert Sungenis, founder of Catholic Apologetics International, is an example of an influential modern geocentrist.
In addition to the minority of stubborn fundamentalists who insist on a geocentric model for dogmatic reasons, there are also a substantial number of undereducated people who hold a kind of passive geocentrism for ignorance, believing (if they even think about it at all) that the Sun must orbit the Earth daily because that is what we appear to see (18% of Americans as of 1999).[21] (As to what the stars are doing, who notices or cares what they are doing? In a light-polluted city night, what's the last time you saw a star?) According to recent polls in the United States, Great Britain and Germany, between 16% and 19% of people actually believe the Sun goes round the Earth.[22]
Debunking geocentrism
Modern geocentrists cite 19th century experiments which tried to measure the mechanical properties of the luminiferous aether (a hypothetical medium in which light would propagate), and got a null result (which is misinterpreted as a null result for the motion of the Earth). Such were the Michelson-Morley experiment![]() and the use of a water-filled telescope by George Biddell Airy. Alas both failed, as the medium whose properties they were trying to measure doesn't exist. Hopefully, the special theory of relativity perfectly accounts for these results in a heliocentric model. The modern rejection of geocentrism can be fairly described by (borrowing a phrase from Dobzhansky), "Nothing in astronomy makes sense except in the light of heliocentrism", leaving the geocentrists with casting doubt on particulars in isolation.
and the use of a water-filled telescope by George Biddell Airy. Alas both failed, as the medium whose properties they were trying to measure doesn't exist. Hopefully, the special theory of relativity perfectly accounts for these results in a heliocentric model. The modern rejection of geocentrism can be fairly described by (borrowing a phrase from Dobzhansky), "Nothing in astronomy makes sense except in the light of heliocentrism", leaving the geocentrists with casting doubt on particulars in isolation.
If, however, one decides to play the game that the geocentrists want, one ought to be aware that they have answers for many of the obvious arguments against geocentrism. Whether or not their answers are sufficient, one should be aware that in pursuing these lines, one is playing on the geocentrists' home field, where they are likely more familiar with the arguments. (If one is as familiar as they are, after all, guidance from RationalWiki.org is not needed.)
Geocentrists' replies to arguments against their position
Geocentrists have some common replies to common arguments against their position:
- They will argue, correctly, that pictures from outer space showing the Earth in motion can be explained by the relative motion from the camera, not absolute motion of Earth.
- They will argue that phenomena that reveal the motion of the Earth, such as the Foucault pendulum
 and the Coriolis effect,
and the Coriolis effect, are accounted for by appealing to something like Mach's principle,
are accounted for by appealing to something like Mach's principle, by which any consequence of rotation of the Earth is the same as would occur with the movement of the "fixed stars" around a fixed Earth.
by which any consequence of rotation of the Earth is the same as would occur with the movement of the "fixed stars" around a fixed Earth.
- Phenomena such as the phases of Venus and Mercury and the apparent retrograde motion
 of Mars (and of the more distant planets) present no problem to modern geocentrism, for it typically adopts Tycho's model (in which those planets orbit the Sun).
of Mars (and of the more distant planets) present no problem to modern geocentrism, for it typically adopts Tycho's model (in which those planets orbit the Sun).
- Any geometric configuration of the Solar System, and thus any kinematic description of its motions, and any dynamic equations which have the Sun as the center, can equally (if not conveniently) be described with a coordinate system with the Earth as the zero point, for example in suitably chosen Lagrangian
 coordinates. (This is done within classical Newtonian mechanics.) Yes, this requires that there be postulated an extraordinary force, which has no known evidence, one which critics would call "ad hoc". For geocentrists, that is worth it. (It has the benefit, for the geocentrists, that few people can follow the mathematics at this point, and those who can are beyond hope of taking geocentrism seriously, anyway.)
coordinates. (This is done within classical Newtonian mechanics.) Yes, this requires that there be postulated an extraordinary force, which has no known evidence, one which critics would call "ad hoc". For geocentrists, that is worth it. (It has the benefit, for the geocentrists, that few people can follow the mathematics at this point, and those who can are beyond hope of taking geocentrism seriously, anyway.)
- Objects as far away as Neptune (whose orbit has a radius of 4 light-hours) would have to move faster than the speed of light to circle the Earth in 24 hours. In response, geocentrists will appeal to the Theory of General Relativity, which permits objects to take on any speed under special circumstances.[23]
- We read about how a major earthquake changes the rotation of the Earth, which proves that the Earth really has a rotation. The geocentrists point out, however, that that is only a calculated estimate, and that we do not have the technology to measure the small differences that are involved.[citation needed] Even if this correlation with earthquakes should become measurable, as long as the cause of earthquakes is not well enough known to predict earthquakes, one cannot rule out that a change in the rotation of the heavens is the cause of earthquakes, or that there is a common cause for both.
Daily rotation of the Earth

One important counterargument to geocentrism is that the rotation of the Earth isn't completely smooth: there is a slight deviation (the Chandler wobble![]() ). The Earth's rotation speeds up and slows down slightly and the point of its axis changes a little.[24]
). The Earth's rotation speeds up and slows down slightly and the point of its axis changes a little.[24]
Heliocentrists can explain this easily: the Earth moves. And as physical conditions change, the motions of the Earth change.
Geocentrists have to imagine that the stars and galaxies all wobble in (what appears to us) synchronicity while Earth stays still. Since these stars and galaxies are millions of light years[notes 2] apart, however, their wobbles must all occur in the same pattern, but at different times according to their distance from Earth so that the light from these different objects reaches us at exactly the same time making it look simultaneous (for example, the apparent wobble of a star 10 light years away would actually be our observation of its wobble 10 years ago, in synchronicity with a coordinated wobble of another star somewhere across the universe 5 light-years in another direction, but that second star only wobbled 5 years ago).
Such a Universe model seriously strains credibility. It's like arguing that you don't actually move but everything else moves and accommodates for your vision changes.
Telescopes not participating in the rotation of Earth
The spacecraft Kepler and Gaia are in orbit around the Sun, and as such do not participate in the rotation of Earth, although they are in the same solar orbit as Earth. They are designed to observe stars to give information such as the existence of exoplanets, or their parallaxes. They are a source of information not dependent on the motion of Earth, and thus when they agree with the results of the heliocentric model, are confirmation of that model.
Position of the Earth at the center of the Universe
In the 14th century, Jean Buridan![]() considered the motion of the Earth, but decided against it. But he did propose an argument against the center of the Universe being the center of the Earth (that, after all, is the literal meaning of "geocentrism"). He observed that the Earth is not symmetrical, that land predominates in one hemisphere (his own) and water in the antipodes. Then, when there is erosion of land into the water, there is a shift in the location of the center of gravity of Earth, which, if the center of gravity of the Earth was the center of the Universe, would require a motion of the Earth to compensate for the change.[19]:165[25]
considered the motion of the Earth, but decided against it. But he did propose an argument against the center of the Universe being the center of the Earth (that, after all, is the literal meaning of "geocentrism"). He observed that the Earth is not symmetrical, that land predominates in one hemisphere (his own) and water in the antipodes. Then, when there is erosion of land into the water, there is a shift in the location of the center of gravity of Earth, which, if the center of gravity of the Earth was the center of the Universe, would require a motion of the Earth to compensate for the change.[19]:165[25]
Denial of the Copernican principle
The geocentric documentary, The Principle, also brings up the later development from heliocentrism, that the Earth is not special, in any way, from anywhere else in the Universe. This is more of a guiding principle than something which can be evidenced. Instances of it include:
- The elimination of the Aristotelian distinction between the sub-lunar sphere of: ordinary matter, earth, water, air and fire; from the lunar sphere (and beyond) of celestial aether. This, we hope, has been established finally and without doubt by interplanetary probes, as if there were any doubt since Newton. If one wants to deny that astronauts walked on the Moon, does one also deny the reality of exploration of Mars and all sorts of Solar System objects? Interplanetary probes, made of terrestrial matter, behave like heavenly bodies when they enter the realm of the heavens. Meteorites (and photons and cosmic rays) behave like terrestrial matter when they land on Earth.
- What is there which makes the Earth different from Mars? Mars is in motion, why not Earth?
See also
- Flat Earth [notes 3]
- Galactocentricity
- Tycho Brahe
- Johannes Kepler
- Galileo Galilei
God himselfIsaac Newton
External links
- Man in the Middle: An Exclusive Cut Excerpt from Rapture Ready! by Daniel Radosh
- Geocentrism Debunked an anti-geocentrist website
- Galileo Was Wrong a geocentrist website
- Geocentric wikia a small geocentrist website
- Trailer for a 2014 geocentric "documentary" movie called The Principle in which physicists (Michio Kaku and Lawrence Krauss) were quote mined. Yes, geocentrists are real, though geocentricity is not.
- Does the Earth move around the Sun? by Sean Carroll
- Testing Geocentrism, a youtube series which, well, puts the claims and ideas of geocentrists, both ancient and modern, to the test.
- Geocentrism? Seriously? by Phil Plait, ‘’Bad Astronomy’’ 2010 September 14
- Geocentrism website
Notes
- ↑ Actually, the problem of faster-than-light travel occurs at the position of the planet Neptune, which has a mean distance of about 4 light-hours, as can be measured by the radio delay of space probes, and thus a path length, circumference = 4×2π > 24 light-hours to traverse in a day.
- ↑ Well, of course, the geocentrists can claim, contrary to all the evidence, that stars are really only little mysterious points of light only a few light years away. (Remember, "nothing in astronomy makes sense except in the light of heliocentrism".) The argument still works, we're saying that stars are making this strangely coordinated dance (the metaphor of the dance is due to the Platonic work Epinomis 982e), instantly changing so that their light will appear on Earth in synchrony. Even if the separation is a matter of as little as days, it is still demanding thousands of ad hoc changes which just happen to look like it is really the Earth which is changing its motions.
- ↑ Flat Earthery is a semi-related form of pseudoastronomy, but note that most people who call themselves geocentrists aren't flat earthers, since the Ptolemaic and Tychonic systems they tend to espouse are built on a round earth foundation. Flat earthers can be said to technically be geocentrists, but since they tend to believe Earth is a flat disk with a hemispherical glass dome (the "firmament"), that the planets are just "lights" in this firmament and not physical places, and that space doesn't exist at all, they're a different sort of geocentrist from the ones described here.
References
- ↑ C. M. Linton (2004). From Eudoxus to Einstein: A History of Mathematical Astronomy. Loughborough, UK: Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ Aristarchus of Samos by J. J. O'Connor & E. F. Robertson (1999) School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St Andrews, Scotland.
- ↑ The Sand Reckoner by Bradley W. Carroll
- ↑ Fourier Series by Eric W. Weisstein. Wolfram MathWorld
- ↑ The Mathematical Power of Epicyclical Astronomy by Hanson, N. R. (1960) Isis, 51, 150.
- ↑ Eastwood, Bruce Stansfield. "Heraclides and heliocentrism: Texts, diagrams, and interpretations." Journal for the History of Astronomy 23.4 (1992): 233.
- ↑ Jump up to: 7.0 7.1 Thomas S. Kuhn (1957). The Copernican Revolution: Planetary Astronomy in the Development of Western Thought. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- ↑ Blair, Ann, "Tycho Brahe's critique of Copernicus and the Copernican system", Journal of the History of Ideas, 51, 1990: 355-377, doi:10.2307/2709620, pages 361-362. Moesgaard, Kristian Peder, "Copernican Influence on Tycho Brahe", The Reception of Copernicus' Heliocentric Theory (Jerzy Dobrzycki, ed.) Dordrecht & Boston: D. Reidel Pub. Co. 1972. ISBN 90-277-0311-6, page 40. Gingerich, Owen, "Copernicus and Tycho", Scientific American 173, 1973: 86 – 101, page 87.
- ↑ Edward Grant, The Foundations of Modern Science in the Middle Ages, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996), pp. 114–16.
- ↑ Aristarchus of Samos
- ↑ Giorgio de Santillana, 1955. The Crime of Galileo pp. 23. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- ↑ "In 1616, the Inquisition placed De revolutionibus on its Index until corrected — Decree XIV. In 1620, in Decree XXI, the required corrections were officially announced. This is an extraordinary measure since for very few books did the Index specify the type of changes to be made. The ten emendations were designed to make Copernicus' book appear hypothetical and not the description of a real physical work."
- ↑ Gingerich, Owen. "The role of Erasmus Reinhold and the Prutenic Tables in the dissemination of Copernican theory." Studia Copernicana 6 (1973): 53-54
- ↑ Owen Gingerich & B. Welther, "The Accuracy of Ephemerides 1500-1800", Vistas in Astronomy, 28 (1985), 339-342
- ↑ Jump up to: 15.0 15.1 On the magnet, magnetick bodies also, and on the great magnet the earth; a new Physiology, demonstrated by many arguments & experiments by William Gilbert of Colchester (1900).
- ↑ Westman, Robert S. "Kepler's early physical-astrological problematic." Journal for the History of Astronomy 32 (2001): 227-236.
- ↑ Optics: Paralipomena to Witelo & Optical Part of Astronomy. translated by William H. Donahue, Green Lion Press: Santa Fe, NM, 2000.
- ↑ Ismael Boulliau by O'Connor, John J. and Roberson, Edmund F. (2006). School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St Andrews, Scotland
- ↑ Jump up to: 19.0 19.1 John Freely (2012). Before Galileo: The Birth of Modern Science in Medieval Europe. New York: Overlook Duckworth. ISBN 9781590206072.
- ↑
Letter to Benedetto Castelli, 1613 December 21, in:
Maurice A. Finocchiaro (1989). The Galileo Affair: A Documentary History. University of California Press. pp. 49–55. ISBN 978-0-520-066662-5.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: length (help) - ↑ New Poll Gauges Americans' General Knowledge Levels: Four-fifths know earth revolves around sun by Steve Crabtree (July 6, 1999) Gallup.
- ↑ New Poll Gauges Americans' General Knowledge Levelsmodern medievalism: Geocentrism
- ↑ An Introduction to the Theory of Relativity, W. G. V. Rosser, London, Butterworths, 1964, p. 460
- ↑ What is the Chandler wobble?
- ↑ Jean Buridan (1964). "Jean Buridan on the Diurnal Rotation of the Earth". Medieval Philosophy: Selected readings from Augustine to Buridan. New York: Modern Library. pp. 542–547. [1]